Making Sense of Shoulder Pain When Breathing Deep: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Understanding What Causes Shoulder Pain When Breathing Deep and What to Do About It
Shoulder pain can be an unsettling when it occurs simply be taking a deep breath. While there are various causes of this pain, we will discuss various underlying conditions, signs and symptoms, and the best shoulder pain treatment options. This blog post will dive into the causes of shoulder pain when breathing deeply, discuss signs that indicate the need to see a doctor, explore common conditions or causes, and discuss various treatment options.
Causes of Shoulder Pain When Breathing Deep
1. Muscular Strain - Overexertion or stress of shoulder muscles, such as heavy lifting or developing poor posture can lead to muscular strains of the shoulder. When surrounding muscles are inflamed, sharp shoulder pains can happen when taking a deep breath.
2. Rotator Cuff Injury - Rotator cuffs are the tendons and muscles that stabilize the shoulder joint. Overuse, repetitive motions, trauma, or degenerative changes such as arthritis can result in a rotator cuff injury, causing pain when breathing deeply.
3. Pleurisy - Pleurisy occurs when the lining around the lungs becomes inflamed. Infections like pneumonia or viral respiratory illnesses can lead to pleurisy. In this condition, taking deep breaths or coughing can cause severe pain in the shoulder or chest. Pleurisy pain is often extreme and occurs with every deep breathe until resolved, which can take hours to get medical treatment.
4. Gallbladder Issues - Shoulder pain when breathing deeply may be a referred pain coming from the gallbladder. Gallbladder inflammation and gallstones can cause discomfort that radiates to the shoulder area and shoulder joint.
Conditions Associated with Shoulder Pain When Breathing Deep
1. Tendonitis - Inflammation of tendons in the shoulder, known as tendonitis, can cause pain during deep breaths.
2. Costrochondritis - Is inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone. Costrochondritis can cause sharp or stabbing shoulder pain.
3. Pneumonia - When the lungs become infected, pneumonia can occur, leading to pleurisy and subsequent shoulder pain when breathing deeply.
4. Gallbladder Disease - Conditions such as gallstones or cholecystitis (gallbladder inflammation) can cause referred pain in the shoulder during deep breathing.
5. Lung Cancer - Rarely shoulder pain during deep breathing can be an unexpected symptom of lung cancer. Shoulder pain in the shoulder blade area that worsens when coughing, taking deep breaths, or laughing may be from the compression of a tumor.
Common Treatments for Shoulder Pain When Breathing Deep
1. Rest and Ice - Muscular strains or injuries are first treated by resting the shoulder and using ice to reduce pain and inflammation.
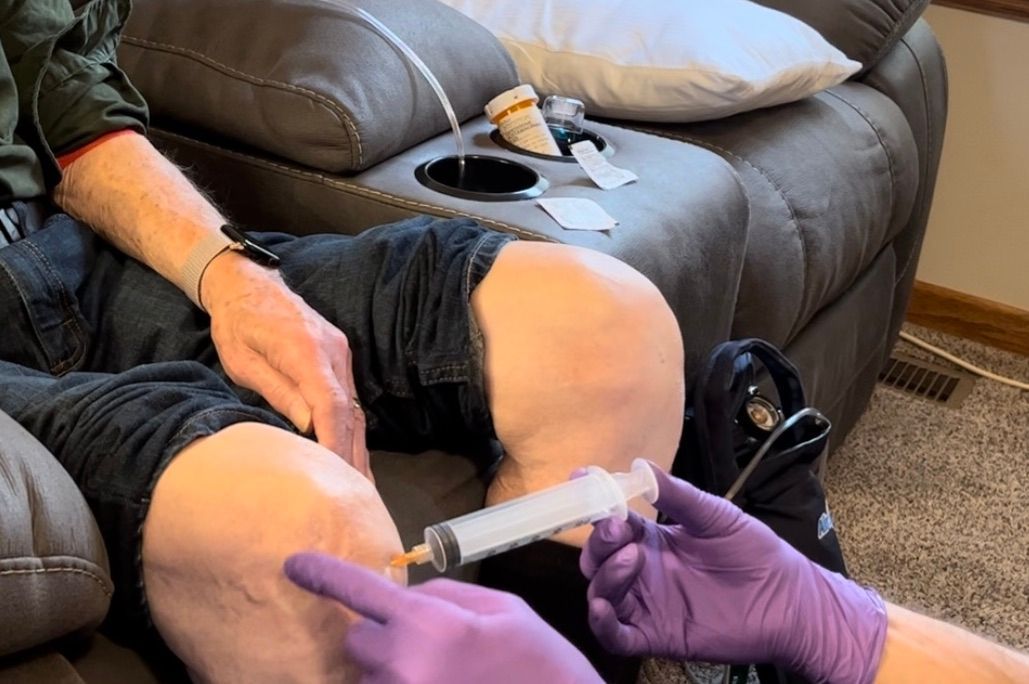
2. Regenerative Injections of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP), Ozone Injections, Dextrose Injections, or Stem Cell Therapy Injections - In rotator cuff injuries or tendonitis, a prolotherapy provider injects the damaged tissues and arthritic joint, improving strength, flexibility, and shoulder function by natural stimulation of the body's innate healing response.
3. Medications - Over the counter Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs can relieve pain and reduce inflammation in minor issues. Prescription medications are used in conjunction with Regenerative Injections of PRP and Ozone.
4. Medical Intervention - If the underlying cause is a specific condition like pneumonia or gallbladder disease, antibiotics, surgery, or more medical care may be required.
Signs that Indicate the Need to See a Doctor
1. Persistent Pain: If the pain lasts several days or intensifies over time, quickly see a healthcare provider.
2. Difficulty Breathing: Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing means its time to seek immediate medical attention, as there could be a severe underlying condition.
3. Limited Shoulder Mobility: If you notice a significant reduction in shoulder mobility or if the pain interferes with your daily activities, seek medical treatment.
Seek Medical Help
Consulting a health care provider is one of the first steps if you have shoulder pain while breathing deeply or even during normal breathing. At One Natural Health we first determine if the pain is likely muscular, which is often the case, or if it is connected to other symptoms that require further care.